|
交叉编译工具文件(cross compiler tool file) Linux程序交叉编译工具:gcc-linaro-5.3-2016.02-x86_64_arm-linux-gnueabihf.tar.xz
Linux program cross compiler tool:gcc-linaro-5.3-2016.02-x86_64_arm-linux-gnueabihf.tar
Linux交叉编译工具配置文件:gcc-linaro-5.3-2016.02-x86_64_arm-linux-gnueabihf-env
Linux cross compiler tool configuration file:gcc-linaro-5.3-2016.02-x86_64_arm-linux-gnueabihf-env
创建工作目录(creat working directory)1)源码目录
source code directory
$ mkdir ~/my-imx6/02_source –p

2)工具目录
tool directory
$ mkdir ~/my-imx6/03_tools –p

3)镜像目录
image directory
$ mkdir ~/my-imx6/04_image –p

$ mkdir ~/my-imx6/04_image/image-linux-4115 –p

4)应用程序目录
application diretory
$ mkdir ~/my-demo

安装交叉编译工具链(install cross compiler tool chain)
安装Linux交叉编译工具链(install Linux cross compiler tool chain)1)进入交叉编译工具链目录
enter cross compiler tool chain diretory
$ cd ~/my-imx6/03_tools/
2)复制Linux交叉编译工具到目录
copy Linux cross compiler tool to directory
将gcc-linaro-5.3-2016.02-x86_64_arm-linux-gnueabihf.tar复制到“~/my-imx6/03_tools”,这一步自己采取相应的方式完成。
3)解压Linux交叉编译工具
copy gcc-linaro-5.3-2016.02-x86_64_arm-linux-gnueabihf.tar to“~/my-imx6/03_tools”,complete this step by yourself in a proper way。
$ tar xf gcc-linaro-5.3-2016.02-x86_64_arm-linux-gnueabihf.tar

4)复制交叉编译工具配置文件
copy cross compiler tool configuration file
将gcc-linaro-5.3-2016.02-x86_64_arm-linux-gnueabihf-env复制到“~/my-imx6/03_tools”,这一步自己采取相应的方式完成。
copy gcc-linaro-5.3-2016.02-x86_64_arm-linux-gnueabihf-env to“~/my-imx6/03_tools”,complete this step by yourself in a proper way。
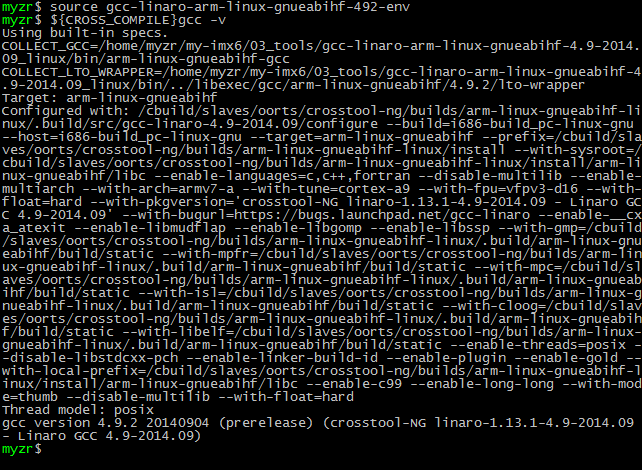
5)检查安装
check installation
$ source gcc-linaro-5.3-2016.02-x86_64_arm-linux-gnueabihf-env
$ ${CROSS_COMPILE}gcc –v
U-Boot编译(U-Boot compilation)
准备编译(prepare compilation)复制源码包到开发主机中(copy source code package to development host)将下载的“u-boot源码”复制到Linux开发主机的“~/my-imx6/02_source”。
copy“u-boot source code”downloaded to “~/my-imx6/02_source”of Linux development host。
这一步自己采取相应的方式完成。
complete this step by yourself in a proper way。
解压u-boot源码包(decompress u-boot source code package)$ cd ~/my-imx6/02_source/
$ tar xf u-boot-2016.03__svn121.tar.xz

编译(compilation)使编译配置文件生效(validate compiler configuration file)$ source ~/my-imx6/03_tools/gcc-linaro-5.3-2016.02-x86_64_arm-linux-gnueabihf-env

进入u-boot源码目录(enter u-boot source code directory)$ cd ~/my-imx6/02_source/u-boot-2016.03

清除u-boot临时文件 (remove u-boot temporary files)$ make distclean

配置u-boot(configure u-boot)configuration of development and its corresponding compiler:
评估板主型号
(development board main model) | CPU类型-内存容量
(CPU type-memory capacity ) | 处理器架构
(architeture of processor) | 对应的u-boot配置
(corresponding u-boot configuration) | | MY-IMX6-EK200 | i.MX 6QuadPlus - 1G | Cortex-A9 | myimx6ek200-6qp_defconfig | | i.MX 6QuadPlus - 2G | Cortex-A9 | myimx6ek200-6qp-2g_defconfig | | i.MX6 Quad - 1G | Cortex-A9 | myimx6ek200-6q_defconfig | | i.MX6 Quad - 2G | Cortex-A9 | myimx6ek200-6q-2g_defconfig | | i.MX6 DualLite - 1G | Cortex-A9 | myimx6ek200-6u_defconfig | | i.MX 6Solo - 512M | Cortex-A9 | myimx6ek200-6s_defconfig | | i.MX 6Solo - 1G | Cortex-A9 | myimx6ek200-6s-1g_defconfig | | MY-IMX6-EK314 | i.MX 6QuadPlus - 1G | Cortex-A9 | myimx6ek200-6qp_defconfig | | i.MX 6QuadPlus - 2G | Cortex-A9 | myimx6ek200-6qp-2g_defconfig | | i.MX6 Quad- 1G | Cortex-A9 | myimx6ek314-6q_defconfig | | i.MX6 Quad- 2G | Cortex-A9 | myimx6ek314-6q-2g_defconfig | | i.MX6 DualLite - 1G | Cortex-A9 | myimx6ek314-6u_defconfig | | MY-IMX6-EK336 | i.MX 6QuadPlus - 1G | Cortex-A9 | myimx6ek336-6qp_defconfig | | i.MX 6QuadPlus - 2G | Cortex-A9 | myimx6ek336-6qp-2g_defconfig | | i.MX6 Quad- 1G | Cortex-A9 | myimx6ek336-6q_defconfig | | i.MX6 Quad- 2G | Cortex-A9 | myimx6ek336-6q-2g_defconfig | | MY-IMX6-EK140 | i.MX 6UltraLite-256M | Cortex-A7 | myimx6ek140-6g_defconfig | | i.MX 6UltraLite-512M | Cortex-A7 | myimx6ek140-6g-512m_defconfig | | i.MX 6UltraLite Full - 256M | Cortex-A7 | myimx6ek140p-6g_defconfig | | i.MX 6UltraLite Full - 512M | Cortex-A7 | myimx6ek140p-6g-512m_defconfig | | i.MX 6UlltraLite Full - 256M | Cortex-A7 | myimx6ek140p-6y_defconfig | | i.MX 6UlltraLite Full - 512M | Cortex-A7 | myimx6ek140p-6y-512m_defconfig |
MYIMX6EK200-6Q-1G configuration example:
$ make myimx6ek200-6q_defconfig
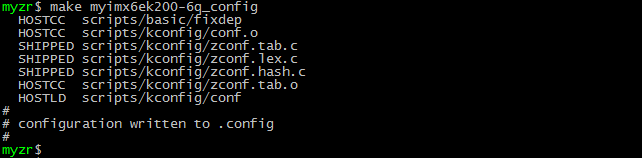
执行编译(execute compilation)$ make
提示:这里为了提高编译速度,在make后面加了“-j4”。这里编译的Linux主机是双核4线程的,所以“-j”后面用了4,也就是采用4线程编译。“-j”后面的数字可以根据系统资源分配,但是不应该超过编译主机最大支持的线程数。
Tips:To speed up the compilation,add "-j4" after make.The Linux host used to compile is dual-core ,4 threads .So "-j" is followed by 4, which takes 4 threads to compile. The number behind "-j" is allocated based on system resources,but It should not exceed the maximum threads the host support.
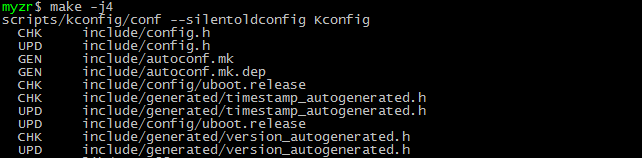
complete compilation
提示:u-boot编译过程大概需要一、两分钟时间。
Tips: u-boot compiling process may take one or two minutes。
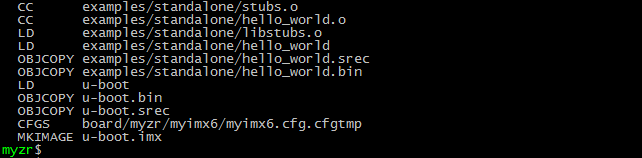
目标文件(target file)compile file
编译完成后通过ls命令即可看到编译得到的文件u-boot.imx
you can get the compiled file u-boot .imx with ls command after compilation.
$ ls
target file
MY-IMX6系列评估板的u-boot配置对应的目标文件名见下表:
The corresponding target file name for u-boot configuration of MY-IMX6 series evaluation board is shown in the table below:
u-boot配置
(u-boot configuration) | 目标文件
(target file) | | myimx6ek200-6qp_defconfig | uboot-myimx6ek200-6qp.imx | | myimx6ek200-6qp-2g_defconfig | uboot-myimx6ek200-6qp-2g.imx | | myimx6ek200-6q_defconfig | uboot-myimx6ek200-6q.imx | | myimx6ek200-6q-2g_defconfig | uboot-myimx6ek200-6q-2g.imx | | myimx6ek200-6u_defconfig | uboot-myimx6ek200-6u.imx | | myimx6ek200-6s_defconfig | uboot-myimx6ek200-6s.imx | | myimx6ek200-6s-1g_defconfig | uboot-myimx6ek200-6s-1g.imx | | | myimx6ek314-6qp_defconfig | uboot-myimx6ek314-6qp.imx | | myimx6ek314-6qp-2g_defconfig | uboot-myimx6ek314-6qp-2g.imx | | myimx6ek314-6q_defconfig | uboot-myimx6ek314-6q.imx | | myimx6ek314-6q-2g_defconfig | uboot-myimx6ek314-6q-2g.imx | | myimx6ek314-6u_defconfig | uboot-myimx6ek314-6u.imx | | | myimx6ek336-6qp_defconfig | uboot-myimx6ek336-6qp.imx | | myimx6ek336-6qp-2g_defconfig | uboot-myimx6ek336-6qp-2g.imx | | myimx6ek336-6q_defconfig | uboot-myimx6ek336-6q.imx | | myimx6ek336-6q-2g_defconfig | uboot-myimx6ek336-6q-2g.imx | | | myimx6ek140-6g_defconfig | uboot-myimx6ek140-6g.imx | | myimx6ek140-6g-512m_defconfig | uboot-myimx6ek140-6g-512m.imx | | myimx6ek140p-6g_defconfig | uboot-myimx6ek140p-6g.imx | | myimx6ek140p-6g-512m_defconfig | uboot-myimx6ek140p-6g-512m.imx | | myimx6ek140p-6y_defconfig | uboot-myimx6ek140p-6y.imx | | myimx6ek140p-6y-512m_defconfig | uboot-myimx6ek140p-6y-512m.imx |
我们需要将编译得到的u-boot.imx复制为我们的目标文件名。
We need to copy the compilied file u-boot.imx as our target file name.:
这里以MY-IMX6-EK200-6Q为例(把配置myimx6ek200-6q_defconfig编译生成的u-boot.imx复制为目标文件):
Copy the generated file u-boot.imx from the compilation of myimx6ek200-6q_defconfig as target file.):
$ cp u-boot.imx ~/my-imx6/04_image/image-linux-4115/uboot-myimx6ek200-6q.imx

编译内核(compile kernel)
准备编译(prepare compilation)复制源码包到开发主机中(copy source code package to development host)将下载的“linux源码”复制到Linux开发主机的“~/my-imx6/02_source”。
copy “linux source code”downloaded to “~/my-imx6/02_source”of Linux development host。
这一步自己采取相应的方式完成。
complete this step by yourself in a proper way。
解压linux源码包(decompress linux source code package)$ cd ~/my-imx6/02_source/
$ tar xf linux-4.1.15__svn189.tar.xz

内核编译配置(kernel compilation configuration)使编译配置文件生效(validate compilfer configuration file)$ source ~/my-imx6/03_tools/gcc-linaro-5.3-2016.02-x86_64_arm-linux-gnueabihf-env

清除内核临时文件(remove kernel temporary file)enter linux source code directory
$ cd ~/my-imx6/02_source/linux-4.1.15

remove temporary file
$ make distclean

内核配置(kernel configuration)kernel configuration file
评估板型号
(evaluation board model) | 配置文件
(configuration file) | | MY-IMX6-EK200 | myimx6a9_defconfig | | MY-IMX6-EK314 | | MY-IMX6-EK336 | | MY-IMX6-EK140 | myimx6a7_defconfig |
$ make myimx6a9_defconfig
如果是编译 MY-IMX6-EK140 的内核,请使用 $ make myimx6a7_defconfig
if what compified is kernel of MY-IMX6-EK140,please use $ make myimx6a7_defconfig
这里以 myimx6a9_defconfig 为例。
take myimx6a9_defconfig as an example。
编译内核(compife kernel)execute compilation
$ make zImage
complete compilation
target file
arch/arm/boot/zImage即为编译得到的内核文件,使用ls命令可查看文件信息。
arch/arm/boot/zImage is the kernel file compifed,you can check file information with ls command。
$ ls arch/arm/boot/zImage -la

注意:我们烧录及启动的内核文件名为“zImage-myimx6a9”或“zImage-myimx6a7”,所以我们需要把zImage复制为zImage-myimx6a9或zImage-myimx6a7。
Note: The kernel file name which is going to be programed and started is “zImage-myimx6” or “zImage-myimx6a7”, So we should copy zImage as zImage-myimx6a9 or zImage-myimx6a7
$ cp arch/arm/boot/zImage ~/my-imx6/04_image/image-linux-4115/zImage-myimx6a9 (A9)
或
$ cp arch/arm/boot/zImage ~/my-imx6/04_image/image-linux-4115/zImage-myimx6a7 (A7)

编译设备树(compife device tree)评估板型号规格与设备树文件对应关系见下表:
The correspondence between the type of evaluation board and device tree is shown below:
评估板主型号
(development main model) | CPU类型-内存容量
(CPU type-memory capacity) | 对应的设备树文件
(corresponding device tree file) | | MY-IMX6-EK200 | i.MX 6QuadPlus - 1G | myimx6ek200-6qp.dtb | | i.MX 6QuadPlus - 2G | myimx6ek200-6qp-2g.dtb | | i.MX6 Quad - 1G | myimx6ek200-6q.dtb | | i.MX6 Quad - 2G | myimx6ek200-6q-2g.dtb | | i.MX6 DualLite - 1G | myimx6ek200-6u.dtb | | i.MX 6Solo - 512M | myimx6ek200-6s.dtb | | i.MX 6Solo - 1G | myimx6ek200-6s-1g.dtb | | MY-IMX6-EK314 | i.MX 6QuadPlus - 1G | myimx6ek314-6qp.dtb | | i.MX 6QuadPlus - 2G | myimx6ek314-6qp-2g.dtb | | i.MX6 Quad - 1G | myimx6ek314-6q.dtb | | i.MX6 Quad - 2G | myimx6ek314-6q-2g.dtb | | i.MX6 DualLite - 1G | myimx6ek314-6u.dtb | | MY-IMX6-EK336 | i.MX 6QuadPlus - 1G | myimx6ek336-6qp.dtb | | i.MX 6QuadPlus - 2G | myimx6ek336-6qp-2g.dtb | | i.MX6 Quad - 1G | myimx6ek336-6q.dtb | | i.MX6 Quad - 2G | myimx6ek336-6q-2g.dtb | | MY-IMX6-EK140 | i.MX 6UltraLite-256M | myimx6ek140-6g.dtb | | i.MX 6UltraLite-512M | myimx6ek140-6g-512m.dtb | | i.MX 6UltraLite Full - 256M (2eth) | myimx6ek140p-6g.dtb | | i.MX 6UltraLite Full - 256M (8uart) | myimx6ek140p-6g-8uart.dtb | | i.MX 6UltraLite Full - 512M (2eth) | myimx6ek140p-6g-512m.dtb | | i.MX 6UltraLite Full - 512M (8uart) | myimx6ek140p-6g-512m-8uart.dtb | | i.MX 6UlltraLite Full - 256M (2eth) | myimx6ek140p-6y.dtb | | i.MX 6UlltraLite Full - 256M (8uart)) | myimx6ek140p-6y-8uart.dtb | | i.MX 6UlltraLite Full - 512M (2eth) | myimx6ek140p-6y-512m.dtb | | i.MX 6UlltraLite Full - 512M (8uart) | myimx6ek140p-6y-512m-8uart.dtb |
take MY-IMX6-EK200-6Q-1G as example
$ make myimx6ek200-6q.dtb

target file
使用ls命令可查看编译得到的目标设备树文件信息:
You can browse the target device tree file information from compilation with ls command:
$ ls arch/arm/boot/dts/myimx6ek*.dtb

复制设备树文件到镜像目录
Copy device tree file to image directory
$ cp arch/arm/boot/dts/myimx6ek*.dtb ~/my-imx6/04_image/image-linux-4115/

编译模块 (compife module)compile module command
$ make modules
Install module to the specified directory
$ make modules_install INSTALL_MOD_PATH=./modules
package the module file
$ cd modules
$ tar cjf ../modules.tar.bz2 *

Copy module package to image directory
评估板型号
(development board model) | 目标模块包
(target module package) | | MY-IMX6-EK200 | kernel-modules-myimx6a9.tar.bz2 | | MY-IMX6-EK314 | | MY-IMX6-EK336 | | MY-IMX6-EK140 | kernel-modules-myimx6a7.tar.bz2 |
$ cp ../modules.tar.bz2 ~/my-imx6/04_image/image-linux-4115/kernel-modules-myimx6a9.tar.bz2
注意:如果是编译内核时配置文件使用的是 myimx6a9_defconfig,在这里要把 modules.tar.bz2 复制为 kernel-modules-myimx6a9.tar.bz2;如果是编译内核时配置文件使用的是 myimx6a7_defconfig,在这里要把 modules.tar.bz2 复制为 kernel-modules-myimx6a7.tar.bz2
Note:when you compile the Kernel If the configuration file you use is myimx6a9_defconfig, here you should Copy modules.tar.bz2 as kernel-modules-myimx6a9.tar.bz2.If the configuration file is myimx6a7_defconfig,you should Copy modules.tar.bz2 as kernel-modules-myimx6a7.tar.bz2.
应用程序编译(application compilation)
Linux应用程序编译(Linux application compilation)编写应用程序(write an application)- 创建应用程序的源码目录和Linux-4.1.15的可执行程序目录
Create application source code directory and Linux-4.1.15 executable program directory
$ mkdir ~/my-demo/source_code -p

$ mkdir ~/my-demo/bin-l4115 -p

write source code
$ cd ~/my-demo/source_code
$ vi hello.c
写入以下代码并保存
write following code and save
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
printf("Hello, MYZR!\n");
return;
}
view code

$ cat hello.c
编译应用程序(compife application)Configure environment variables
$ source ~/my-imx6/03_tools/gcc-linaro-5.3-2016.02-x86_64_arm-linux-gnueabihf-env

compife
$ ${CROSS_COMPILE}gcc hello.c -o hello.out

注意:上面的命令有包含“$”号,即“${CROSS_COMPILE}gcc”,是引用我们source时产生的环境变量。
Note:The above command contains “$”,which is “${CROSS_COMPILE}gcc”. It is the environment variable generated when referring to our source.。
target file
$ file hello.out
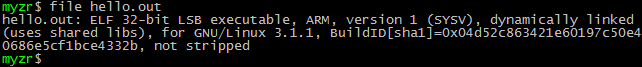
可以看到目标文件 hello.out 的属性。
you can see the property of target file hello.out。
保存目标可执行文件(save target executable file)$ mv hello.out ~/my-demo/bin-l31452/

应用程序打包(package application)说明(instruction)烧录工具支持烧录“my-demo.tar.xz”的文件包到评估板。所以在这里我们把我们需要的应用程序打包为“my-demo.tar.xz”。至于“my-demo.tar.xz”会被烧录到哪个位置,请看《烧录手册》。
Programming tool supports to program “my-demo.tar.xz” file package to evaluation board.So We package applications We need as “my-demo.tar.xz”.while where “my-demo.tar.xz” will be programmed ,refer to 《programming manual》。
打包应用程序(package application)1)打包
package
这里我们将整个my-demo目录打包。
Here We package the whole my-demo directory。
$ cd ~
$ tar cjf my-demo.tar.bz2 my-demo

2)复制应用程序包为目标烧录文件
Copy application package as target programming file
$ cp my-demo.tar.bz2 ~/my-imx6/04_image/image-linux-31452/

目标烧录文件(target programming file)
至此,我们在“~/my-imx6/04_image/image-linux-31452/”得到了除文件系统以外的一套烧录文件。包括“uboot*.imx”、“myimx6*.dtb”、“zImage-myimx6”、“kernel-modules.tar.bz2”、“my-demo.tar.bz2”。
So far,we get a set of programming file except file system from“~/my-imx6/04_image/image-linux-31452/”。including“uboot*.imx”、“myimx6*.dtb”、“zImage-myimx6”、“kernel-modules.tar.bz2”、“my-demo.tar.bz2”。
现在可以参照《烧录手册》烧录我们自己编译出来的image了。
Now we can program the image we compiled by ourselves referring to 《programming manual》.
|  /3
/3 
 /3
/3 